Comparing CO2 Emissions in Carbon Counting Tools due to Natural Gas and Electricity
The tools that were selected had different input and output screens, sometimes with different input requirements, so some assumptions had to be made. The values in Table 3 were input in each of the tools to compare them. Not all of the tools provided results that could be compared between each other (e.g. planets vs kilograms) so only those that had the option to provide a reasonable input and output were compared.
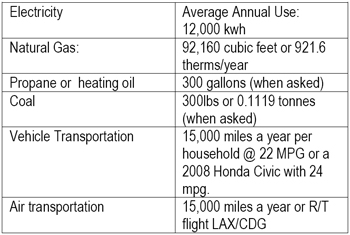
Table 3: Inputs for the Carbon Counting Tools
The carbon calculators that were compared all give different CO2 emissions (Figs 1 & 2), especially for electricity. There is much variation in the results. For electricity the emissions ranged from 6,000 lbs of CO2 per year to 13,000 lbs of CO2 per year and for gas it ranged from 8,600 lbs of C02 / year to 12,000 lbs of CO2 / year. Unfortunately most of these tools are not transparent and it is not easy to determine the equations and conversion factors used for calculations. The average result for natural gas was 11,630 lbs of CO2 for the 921.6 Therms of gas, equivalent to 12.62 lbs of CO2 per Therm, or 0.47 lbs CO2/kWhr, close to the value of 0.418 lbs of CO2 / kWhr proposed by DEFRA (3). The average value for electricity was 11,630 lbs of CO2 per 12,000 KWhr, or 0.97 lbs / Kwhr. As a reference, the average emission factor from grid electricity in the USA was 1.363 lbs / kWh (4). This variability in the calculators indicates that it is probably better to select a conversion factor and multiply this factor by the calculated or recorded energy used in the building.
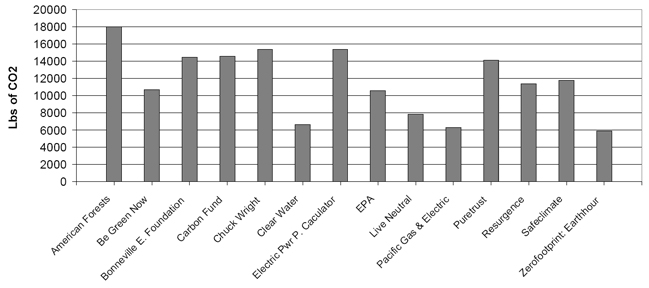
Figure 1: CO2 emissions due to electricity (12,000 Kwh)
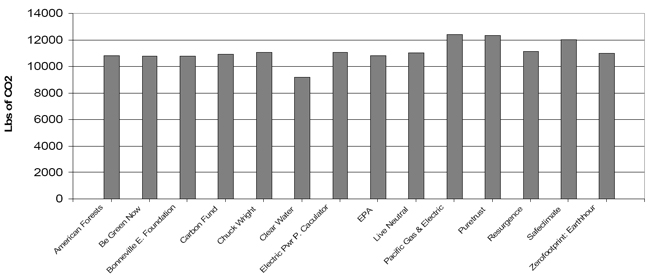
Figure 2: CO2 Emissions due to natural gas (921 Therms) |

